A Complete Guide on Multi-Agent Testing

- February 24, 2026
- Nabeesha Javed
Most CTO’s, QA engineers, and DevOps teams still limit LLM usage to basic tasks like generating test cases or BDD scenarios, rather than leveraging their full automation potential. While AI usage in software testing rose from 7% in 2023 to 16% by mid-2025, a large majority of organizations are still only in the piloting or experimentation phase, not full production.
Major Problems with Adding AI Agentic Testing Workflows
Some issues arise when QA engineers integrate AI into testing workflows:
- Cloud AI models have token and file size limits, which restrict large test logs, reports, and datasets.
- While technologies like LangChain, Playwright, and AI agents are gaining popularity, practical implementation guidance for real-world QA use cases remains limited.
- Even with automation in place, teams struggle with log analysis, root cause analysis, test case generation, and requirement traceability.
- Many teams lack a clear understanding of how to design and manage AI multi-agent systems effectively.
- Handling structured and unstructured test data is complex and often requires writing difficult queries to extract useful insights.
Struggling to move beyond AI testing experiments? At Kulaitatem, we help teams turn ideas into production-ready AI automation testing services with clear processes and measurable outcomes.
How the QA Testing Industry is Responding to AI Agents
According to McKinsey & Company research, 82% of QA professionals believe AI skills will be critical for the future of testing. However, many still underestimate the shift from “human-directed” (AI-assisted) to “human-verified” (AI-autonomous) models of work.
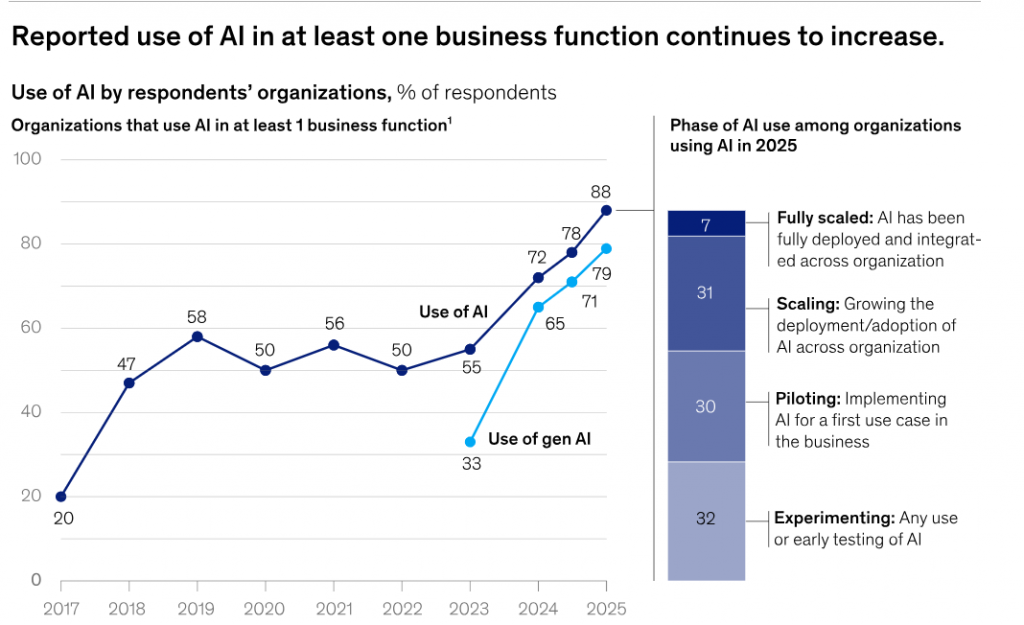
The Mickensy data from article State of AI 2026 report shows that 62% of testers are still piloting and experimenting use of AI as a early stage. Even though other industries are adopting AI agents fast, the software testing industry is still at a very early stage.
Most organizations are either not using AI agents at all or are just beginning to experiment. This suggests a large opportunity gap; despite the hype around AI-driven testing, enterprise-level implementation remains limited.
Furthermore, if we look at the opinion of 50% of AI leaders or Automation Experts who have scaled with AI agents, they expect AI to drive transformative change. In contrast, 48% of other companies expect only incremental improvements.
“Successful companies are not using AI as a tool but treat AI as a core part of their strategy and future growth.”
Kualitatem, Inc
Multi-Agent System Testing Guide: Benefits
If you aim to lead engineering teams building AI-powered QA systems, this guide provides practical and strategic insights.
- Empowers QA Engineers with AI agent capabilities to move beyond prompt engineering
- Uses local large language models
- Practical, QA & leadership-focused implementation
- Understand real AI-Powered QA tools
- AI Web Scraper (Playwright-Based)
- Retrieval-Based QA System
- Learn LangChain & Microsoft AutoGen
- Understand AI agent architecture
- Multi-Agent Collaboration
- Improve QA Productivity & Quality of Life
Let’s start by understanding the core concepts
What is Multi-Agent AI Testing?
In multi-agent system testing, multiple AI agents collaborate (or sometimes compete) to achieve shared testing objectives. All agents coordinate as a team to accomplish tasks.
- One agent may parse requirements.
- Another may generate test cases.
- A third may simulate user behavior.
| Single-Agent AI Testing | Multi-Agent AI Testing |
| Automates a single QA task, such as generating test cases or analyzing logs. | Automates multiple QA tasks at the same time, like generating test cases, analyzing logs, and simulating user behavior. |
| Works independently without coordinating with other tools or agents. | Agents work together, passing information and coordinating to complete complex QA workflows. |
| Can catch errors within its specific task only. | Can find system-level issues, integration problems, and unexpected errors caused by interactions between agents. |
| Testing and QA improvements are limited to the agent’s individual capability. | Testing and QA improvements cover the whole process, providing smarter, more comprehensive automation. |
| Easier to implement but offers limited scalability. | More complex to implement but scales to handle large, multi-step QA workflows. |
| Best for simple, repetitive QA tasks. | Best for complex testing scenarios that require collaboration and orchestration. |
Challenges of Multi-Agent QA
- Agent interactions are dynamic and context-dependent.
- Traditional tests assume fixed flows, but agents can negotiate tasks or change behavior.
- Effective testing requires new strategies:
- End-to-end user-journey tests
- Injecting failures at protocol boundaries
- Chaos testing of agent communications
Core Capabilities of AI Testing Agents
AI Testing Agents make traditional automation much smarter. They can do things that normal automation can’t. Here’s what they can do
- Adaptive Learning
They learn from past test runs and feedback. If something fails or a UI changes, they adjust automatically.
- Parallelism & Coverage
Agents can run tests at the same time (e.g., one for web, one for API), covering more ground faster.
- Testing Specialization
Agents can focus on different tasks (UI, API, database) and coordinate via a lead agent
- Natural-Language Interface
You can give them plain-English instructions like “Test login functionality,” and they’ll turn it into test steps.
- Self-Healing
If a test breaks because an element moved or an ID changed, they figure out a way to continue instead of just failing.
- Intelligent Prioritization
They look at code changes and risks to decide which tests are most important to run first.
- Collaborative Problem-Solving
In a multi-agent setup, agents can work together like a team one handles data, another handles test logic, and so on.
- Scalable Test Coverage
They can simulate many user actions or run tests in parallel, covering more in less time.
Tools and Frameworks of Multi-Agent Testing
LangChain
LangChain is a Python framework that helps you connect large language models (LLMs) to tools, data, and custom logic. It’s like a bridge between AI and real-world testing tasks.
LangChain integrates with tools like Playwright, letting QA engineers script browsers programmatically. For example, NavigateTool moves to a page, and ClickTool clicks buttons or links. Agents can also extract text or page elements.
LangChain is great for building step by step workflows. This makes it ideal for predictable QA tasks where actions need to happen in order. It provides ready-made “agents” that can carry out tasks automatically. The new create_agent API (1.0) makes it easier to set up these agents.
- In order to deploy and install dependencies (pip install langchain playwright)
- from langchain.agents import create_agent

For complex flows that need to remember state or context, LangGraph helps manage and coordinate the sequence of tasks. LangChain can do things like web searches or query knowledge graphs (like Wikipedia) and easily connects to common LLM providers.
AutoGen
AutoGen is a framework from Microsoft designed specifically for multi-agent workflows. Imagine instead of building one smart AI, you build a team of AI agents that talk to each other like coworkers.
With AutoGen, you can:
- Create multiple AI agents.
- Give each agent a specific role.
- Let them chat with each other to solve a problem.
- Optionally step in as a human if needed.
You could create agents like:
- RequirementAnalyser
- TestCaseGenerator
- LogChecker
- LeadAgent
These agents automatically pass messages to each other just like testers sharing updates.
Why AutoGen Is Powerful
AutoGen provides AgentChat APIs, which allow agents to send messages,
- Respond to each other
- Collaborate dynamically
- AutoGen v0.4 uses an asynchronous, event-driven architecture.
- Let agents work fully automatically
- Design agent conversations visually
This is helpful for QA teams that want control over decisions. Great for experimentation and debugging. AutoGen is less strict compared to some workflow frameworks.
Instead of forcing a fixed step-by-step flow, it gives agents a role and lets them collaborate naturally. This makes it ideal for complex workflows, research tasks, exploratory QA scenarios, and multi-step problem solving.
OpenAI Agents SDK
The OpenAI Agents SDK (formerly called Swarm) is a lightweight Python framework for building multi-agent systems.
Imagine AutoGen is a full team management system and the OpenAI Agents SDK is a lightweight toolkit to quickly build small AI teams. It gives you just the essential building blocks, nothing much heavy.
The SDK mainly provides three things:

- Agents
- Handoffs
- Guardrails
The OpenAI Agents SDK is great when you want to quickly prototype agent workflows, create controlled agent loops, and build simple multi-step GPT pipelines. Furthermore, if you want to add validation checks between steps
For example:
→ Agent 1 generates test cases.
→ Guardrail checks formatting.
→ Agent 2 validates completeness.
→ Agent 3 summarizes output.
Features of OpenAI Agents SDK
- Built-in tracing (you can see what agents are doing).
- Designed for real-world usage.
- Simple architecture
It mainly works with OpenAI models. It’s not as flexible for non-OpenAI model ecosystems. In contrast, it is different from other frameworks because it is lighter than AutoGen, it is way more structured than pure LangChain flows, and less orchestration-heavy for faster prototyping. If AutoGen feels like building a company, this SDK feels like building a small efficient team with clear task delegation.
Ollama (Running Models Locally)
Ollama helps you run open-source large language models (LLMs) on your own machine. Simply, instead of calling OpenAI or another cloud API, you run the AI model locally. This is mostly useful for Data privacy (no external API calls) at a lower cost, working offline and avoiding token limits.

For example:
- You can start a model using the Ollama CLI.
- You can launch a local API server.
- Your agents can then connect to that local model.
This allows QA teams to use models like Gemma, Claude (if supported locally), Other quantized open-source models. All without sending data outside the organization.
Playwright (Browser Automation)
Playwright is used for browser automation. It allows AI agents to click buttons, fill forms, navigate pages and validate UI elements.

When integrated with:
- LangChain
- AutoGen
It enables AI agents to act like real users in the browser. So your AI agent doesn’t just “think” it actually interacts with the UI.
You can also wrap traditional QA tools and expose them to agents, such as:
- Selenium
- Appium
- REST API clients
- Database connectors
This means your AI agent can call these tools just like a function. So, agents can run API tests, trigger mobile automation, query databases and validate backend responses.
How to Choose Between These Frameworks
When selecting a framework, QA teams should think about:
- How workflows are structured
- How agents cooperate
- Whether conversations or strict pipelines are needed
Look at the matrix comparison table at the end of this blog to understand your scenario and best framework.
Architecting Multi-Agent Systems for Software Testing
Think of multi-agent QA architecture as a way of designing your QA system, not a product. Imagine a software QA system as a city. Each agent is like a specialized worker, but they don’t act in isolation, they’re coordinated, remember context, use specialized tools and feed results into a central CI/CD pipeline. Here’s how it’s structured:
A. Orchestration Layer
The first layer acts as the “city planner,” deciding which agent does what and in what order. It includes a scheduler for automated test runs. Task distributor to specialized agents (e.g., API tester, UI tester, security tester). Monitors progress and dynamically reallocates tasks.
For Example: Instead of one monolithic test suite, orchestration dynamically spins up agents for critical paths or high-risk areas.
B. Memory Layer
The memory layer provides context and persistence for agents. Moreover, this stores previous test results, bug reports, or learned patterns. Allows agents to reason based on history (e.g., “This API has failed in the past under X conditions”). Through these layers, companies can reduce duplicate work, enable intelligent regression testing, and allow agents to adapt over time.
Building multi-agent QA architecture can feel complex. Kulaitatem’s TMMI Level 5 experts help you design scalable AI testing services for your custom frameworks while keeping governance and quality intact. We integrate modern AI tools into your pipelines so you can reduce time-to-market, improve coverage, and ship with confidence.
C. Tool Layer
Tool as discussed above, are a catalyst for agents’ access to specialized AI test automation tools they need to execute their work.
Examples:
- Browser automation (Selenium, Playwright)
- API testing (Postman, REST-assured)
- Security scanning (OWASP ZAP, SAST/DAST tools)
- Load/performance tools (JMeter, Locust)
D. Test Execution Layer
This is the “factory floor” where the actual tests are executed. Significantly faster and more adaptive than scripted sequential automation.
- Agents can run tests in parallel or sequence.
- Can perform exploratory testing using AI to detect edge cases.
- Supports multiple environments: staging, cloud, containers.
E. CI/CD Integration
This layer connects the multi-agent system to your delivery pipeline. You need to execute this layer.
- Automatically triggers QA runs on code commits, merges, or nightly builds.
- Feeds results back to developers, dashboards, and ticketing systems.
- Can decide which tests are critical vs optional, based on AI predictions.
Through this, QA teams become a continuous, intelligent feedback loop rather than a static release gate.
Centralized AI vs Distributed Agent Networks
- Centralized AI: One big model handles all QA tasks.
- Pros: Simple coordination.
- Cons: Bottleneck, less scalable, less flexible.
- Distributed Agent Networks: Multiple specialized AI agents communicate and collaborate.
- Pros: Scalable, resilient, adaptable to complex systems.
- CTO Insight: For large-scale enterprise apps, distributed agents outperform single AI models.
- Pros: Scalable, resilient, adaptable to complex systems.
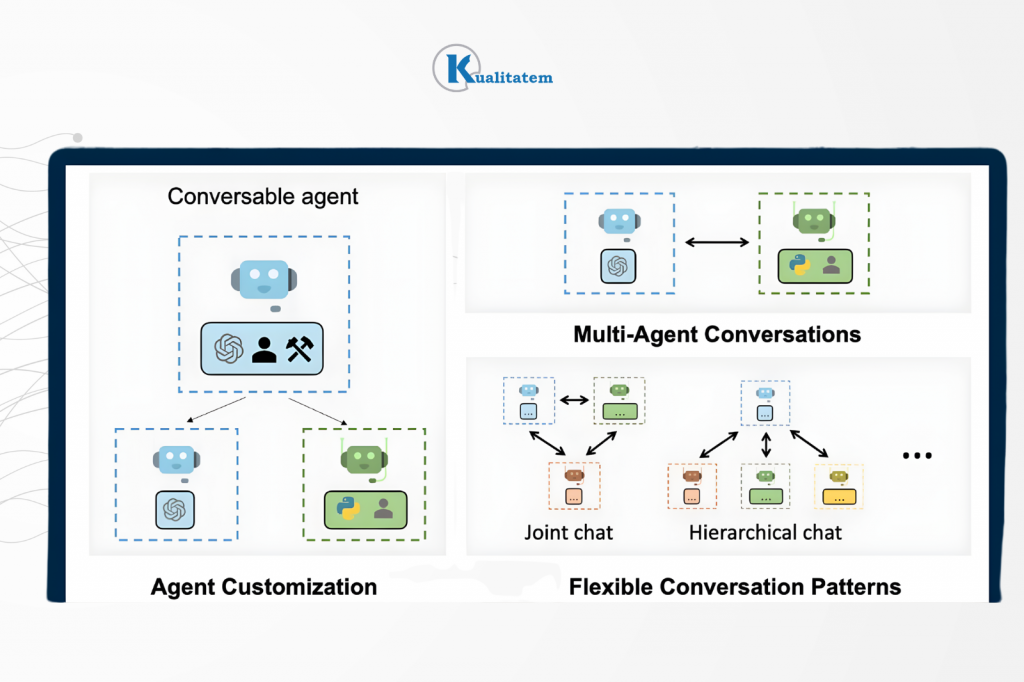
Agentic Test Automation vs Script-Based Automation
- Script-Based Automation is traditional Selenium/Cypress scripts that run tests sequentially.
- Agentic Automation is AI-driven agents that decide what, when, and how to test, adaptively.
Implementing Multi-Agent Testing In Your Workflow
Here are some recommendations for CTOs’ Project Managers before deploying multi-agent testing in their Dev/Ops.
Start Small with Agents
Approve pilot projects in low-risk areas, like regression smoke tests or small feature modules.
Tell QA engineers to implement a single-agent workflow first (e.g., LangChain for automated test generation). Once it works reliably, add more agents for parallel tasks like log analysis or UI automation.
Use Prebuilt Agent Tools
Encourage teams to leverage existing agent tools instead of building everything from scratch. Let team use agents for common QA tasks, such as:
- Jira/Confluence requirement parsing
- Playwright browser automation
- Log parsing agents
This saves development time and accelerates pipeline setup.
Embrace Continuous Learning
Support periodic retraining and updates for AI agents. Allocate resources for monitoring and improving AI workflows. Let QA automation engineers feed multi-agentic AI recent test results, failures, and requirement changes. Ensure agents adapt to new information automatically to reduce repeated errors.
Prioritize High-Value Tests
Guide teams to focus on critical scenarios rather than automating everything at once. Use agent intelligence to identify risk areas, scan code changes, and determine which tests to re-run or generate next.
Measure & Monitor Performance
Track overall ROI of agentic QA. Compare metrics like cycle time, coverage, and defect detection rates against previous manual processes. Log multi-agent agent activities, test coverage, failures caught and maintenance effort. Adjust workflows based on performance data.
Plan for Edge Cases & Human Oversight
Ensure critical decisions, exploratory testing, and high-risk paths always have human approval. Use agents to to augment your work, not replace testers. Include humans in the loop for verification and decision-making in edge cases.
Want to adopt multi-agent testing without long trial-and-error cycles? Kulaitatem helps you implement intelligent automation that fits your product, team, and delivery goals.
Comparing Frameworks for AI-Powered QA
| Scenario | Use LangChain | Use AutoGen | Local LLM (Ollama) | Use Cloud LLM |
| Step-by-step test workflows (API chains, ETL validation, regression flows) | ✅ Best choice Designed for structured pipelines | ❌ Not ideal – Overkill for linear flows | Optional | Optional |
| Multi-role collaboration (Tester ↔ Dev ↔ Reviewer agents) | ⚠ Possible but limited | ✅ Best choice – Built for agent conversations | Optional | Recommended for better reasoning |
| RAG-based test case generation | ✅ Strong support for RAG pipelines | ⚠ Possible but less structured | Good for cost control | Better for complex reasoning |
| UI automation with browser control | ✅ Works well with Playwright tools | ✅ Can coordinate UI + reasoning agents | Good for secure environments | Useful if UI logic is complex |
| Cost-sensitive projects | ✅ Efficient | ⚠ Depends on agent count | ✅ Best option – No API cost | ❌ Higher ongoing cost |
| High-security / On-prem data | ✅Great | ✅Excellent | ✅ Best option (Data stays internal) | ❌ May violate data policies |
| Complex reasoning / Ambiguous requirements | ⚠ Limited by workflow structure | ✅ Strong collaboration capability | ⚠ Depends on model quality | ✅ Best reasoning performance |
| Scaling to many interacting agents | ⚠ More manual coordination needed | ✅ Designed for scaling multi-agent systems | Optional | Recommended |
| CI/CD integration | ✅ Strong pipeline fit | ⚠ Requires more setup | Optional | Optional |
| Rapid prototyping agent loops | ✅ Simple setup (1.0 agents API) | ✅ Good for conversational prototypes | Good | Good |
Executive Summary:
- Use LangChain for structured pipelines
- Use AutoGen for collaboration-heavy workflows
- Use Ollama for secure on-prem environments
- Use cloud LLMs for complex reasoning
Practical Tips for QA Engineers to Integrate Multi-Agent into Testing
Requirement-to-Test Automation
Let an agent read requirement docs (PDFs, Word, Jira tickets) and generate structured test cases automatically (BDD/Gherkin).
- Start with simple modules before scaling to full projects.
Log & Output Analysis
Use a LogAnalyzer agent to scan runtime logs or test reports for errors and performance issues. Pair it with a TestCaseGenerator agent to suggest new checks automatically.
UI End-to-End Testing
Assign agents to browser tasks via Playwright or Selenium (login, checkout, search). Use multiple agents for parallel flows, coordinated by a lead agent.
Multi-Agent QA Loops
Create small “agent groups” that mimic team collaboration:
- UserProxy → Assistant → Verifier
Automate regression or exploratory testing using these loops.
Parallel Models / Ensemble Testing
Run tests on local + cloud models in parallel to find more unique issues (~45% more).
Use local models for speed, cloud models for complex reasoning.
AutoGen Studio Flows (Low-Code)
- Use drag-and-drop visual workflows to connect agents. Example: Requirement → TestCaseGen → ExecuteTest → SummarizeResults. Leverage auto-generated tools like PDF readers or web crawlers to save coding effort.
About us:
Kualitatem has set a long-standing benchmark for excellence in providing test automation as a service. We provide a triple-layer of trust through our internationally recognized certifications, including ISO 27001 for data security, ISO 9001 for process integrity, and TMMi Level 5 for world-class testing maturity.