How to Audit Your Enterprise’s Endpoint Security

- October 4, 2024
- admin
Your endpoint security can be your first line of defense against cyber attacks. But do you know how to check if your endpoints are actually secure? With remote work, BYOD (Bring Your Own Device), and a whole host of IoT devices added to the typical business environment, endpoints are prime targets for hackers. Read on How to Audit Your Enterprise’s Endpoint Security
That’s where an endpoint security audit comes in. An audit helps you identify vulnerabilities, assess the effectiveness of your current security policy, and it’s vital to keep your company compliant with evolving cybersecurity regulations. At Kualitatem, we’ve put our 15+ years of experience into developing a reliable and repeatable framework to execute such audits.
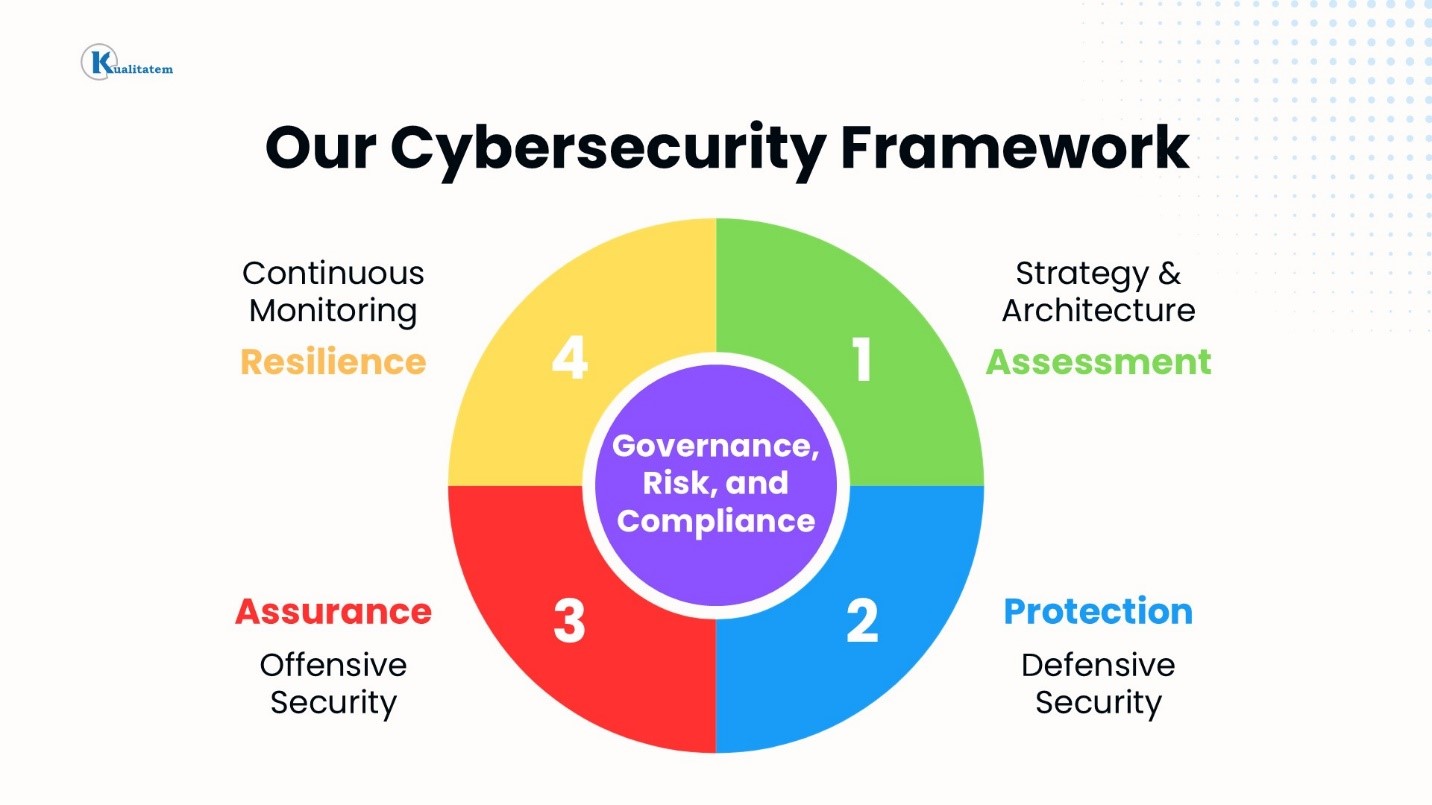
Assessment
1. Inventory Endpoints
Develop a thorough, updated list of all devices connected to your network. This includes the usual suspects – servers, virtual machines, and workstations – but don’t forget your IoT devices such as security cameras, printers, smart speakers, smart TV, and access controllers. If employees can connect to your organization’s network using their mobile devices, include those too.
An automated asset management tool or a robust endpoint security system can really help here by streamlining the inventory process and helping you keep track of all your organization’s endpoints.
2. Review Security Policies
Once your endpoints are logged, you need to review the security policies that govern them. This is important not only for your security assessment but also to ensure you’re in compliance with industry regulations and best practices.
Key areas of your security policy include:
- Antivirus/Anti-malware Protection: Are all devices equipped with updated antivirus and anti-malware software?
- Firewalls: Are firewalls enabled and configured correctly on all endpoints?
- Data Encryption: Is data transmission and storage encrypted on each device?
- Access Control: Is each device secured against unauthorized access via appropriate measures such as passwords and MFA?
- Zero-Trust: Does each endpoint operate with a zero-trust approach that protects against vulnerabilities in both known and unknown programs?
Protection
1. Patching
If you’ve got outdated software and unpatched vulnerabilities in your enterprise environment, it’s not a question of if they’ll be exploited but when. As part of your audit, you need to determine patch status and identify missed patches for prompt execution for every software allowed to run within your environment – and for operating systems as well. A patch management tool can find and help address outdated software quickly.
2. Access Authorization
Your endpoints aren’t secure if they’re not secure against unauthorized access – including both remote access over the Internet and physical access. As part of your audit, you must review access permissions for each user and device. Apply the principle of Least Privilege to give users access to only what’s required for their role.
Besides Role-based Access Control (RBAC) and Multi-factor Authentication (MFA), an important but often overlooked aspect of access control is access logging. Access logs add an element of accountability to your enterprise environment as access is tracked and users can be held accountable for malicious access through their devices and credentials. This promotes a sense of personal responsibility.
Assurance
1. Test Your Security Measures
If your security can’t be tested, your security can’t be trusted. To meaningfully audit your security controls, plan and execute security tests. Some of these tests include:
- Penetration Testing: These sophisticated tests simulate attacks on your endpoints and give you an idea of the performance of your security in the event of a real attack.
- Vulnerability Scanning: A vulnerability scan seeks known weaknesses and common misconfigurations in your endpoints.
- Incident Response Drills: Test your incident response plan to ensure your team is prepared to react quickly to a breach.
If you want unbiased, expert assurance consider engaging an external team to help lead some or all of these tests.
Resilience
1. Monitor Endpoints
Real-time, continuous monitoring is the only effectives form of monitoring against cybersecurity threats. Implementing this can cut down on your team’s response time as well, in case of an actual incident. We covered the benefits of such monitoring in the case study of our client here, who were able to discover a malicious intruder within 10 days of breach – instead of the average 108 days.
When evaluating your organization’s monitoring protocols and needs, look into:
- Logging: Are endpoint activities logged so they can be analyzed for unusual patterns or behaviors?
- Centralized Management: Do you have a centralized dashboard or Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) system to monitor endpoint security alerts?
Given the multitude of endpoints in the modern enterprise environment, it isn’t humanly possible to continuously monitor each endpoint by an individual team member. This is another area where an endpoint security solution such as ThreatLocker shines.
Governance
1. Ensure Compliance
Compliance isn’t just a necessity of doing business – it can help save your organization from significant legal, reputational, and financial damage by reducing your cyber security risks.
Regulations vary by region, so be sure to check in with your legal team to understand which ones apply to your organization. For most regulations, documenting your audit process and results can often jump-start your compliance.
2. Educate Employees
The weakest link in your security strategy isn’t technology. It’s the human element. You can improve this by raising awareness and educating your team about:
- Recognizing phishing attempts and social engineering tactics
- Following endpoint security best practices
- Reporting suspicious activities
Regular training sessions can help keep security at the forefront of your team’s work practices. Another way to keep your team on their toes is to simulate phishing attacks. Incentivizing superior security practices can also help change behavior, as can gamification of the process – for example, through badges and recognition of employees who adopt the greatest security posture.
3. Remediation Planning
A key element of your governance, risk, and compliance protocols is remediation planning. Develop a clear and comprehensive plan that prioritized actions based on risk levels. Your plan should identify and address critical vulnerabilities that provide a timeline for resolving lower-priority issues. Be sure to regularly review and update your plan as threats evolve.
Takeaways
Auditing your organization’s endpoint security is the foundation of a proactive cybersecurity strategy. This is a continuous process that requires a methodical approach. Regular audits supporting by a world-class toolkit or comprehensive endpoint security solution can help identify weaknesses, ensure compliance, and empower your organization to adapt to evolving threats.
Join us for our free webinar session happening _______ on how stop hackers by thinking like a hacker, and implementing a zero-trust solution in your enterprise environment.
Take the guesswork out of cybersecurity. Kualitatem has been involved in several Compromise Assessment assignments with BFSI. Reach out to Kualitatem today to discuss our Security And Risk Assessment | Testing Services | Kualitatem services and discover why 500+ clients trust us to ensure the safety of their most valuable technological assets.